Physics Week#4 The famous E=mc2, four forces, and function of gravity
How has e=mc2 affected you?
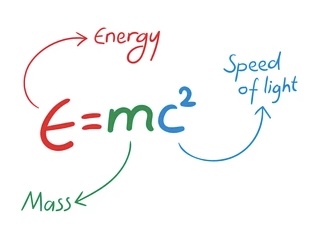
E=mc2, Energy = mass x (speed of light)2, probably is the most famous equation in the world. It has many effects on us. E=mc2 is at work all the time. When I listen to podcasts, my iPhone drains the battery to produce energy in the form of sound waves by converting the battery mass into energy. When I drive my SUV, the engine burns gasoline to produce energy in the form of motion by converting the gasoline’s mass into energy. We can come up with a lot of examples.
How would you compare the four “forces”?
In physics, there are four fundamental forces of nature. They are gravity, electromagnetism, the weak nuclear force and the strong nuclear force. Even we may not realize them, we experience these four interactions every day. Gravity acts between two masses. Although every object in this universe applies this force on all other objects, this is the weakest force. Electromagnetism is the combined impact of electromagnetism and magnetism. It produces a magnetic force besides the electric force when an electric charge is moving. It is stronger than gravity. Weak nuclear force is responsible for the emission of beta particles from the nucleus. It is more powerful than the gravity, but weaker than electromagnetism. Strong nuclear force acts on two nucleons in the nucleus and it is the strongest force in the nature. With the exception of gravity, the three forces are to generate a field affecting behavior of distant objects instead of interacting directly. In the quantum world, these fields are associated with one or more particles. They are the result of some fundamental symmetries of nature.
What is the function of gravity?
Gravity is the attraction between two objects that have mass or energy. Inspired by an apple falling from a tree, Newton was the first to put forward the idea of gravity as an attraction between two objects. Einstein later suggests by his theory of general relativity, gravity is a consequence of objects being space-time. We see gravity all the time in our everyday life, such as a falling leaf, a dropping rock dropping, the rising ocean tides. Not only does it hold things on our planet earth, but also the planets, stars, galaxies together. Regardless of its obvious presence, it is the weakest of the four forces, and almost no significant effect relative to the other fundamental forces.



good examples of gravity! It is always around us so much that we hardly notice, much like a fish not noticing the water he swims in.
ReplyDelete